The first solar eclipse of 2026 will occur on February 17, bringing the rare and visually striking annular solar eclipse, widely known as the “Ring of Fire.” The celestial event has drawn global attention because the Moon will cover most of the Sun while leaving a bright ring of light visible around its edges. However, despite the excitement, the eclipse will not be visible in India, as the path of annularity lies almost entirely in the Southern Hemisphere.
The event will be seen mainly over Antarctica and nearby ocean regions, with only partial visibility in parts of southern Africa and southern South America. Here is a complete, verified and detailed guide covering date, timings, visibility, scientific explanation, safety rules, cultural aspects and upcoming eclipse events.
Key Highlights of Annular Solar Eclipse February 17, 2026: Date, Time, Visibility and India Impact
- The first solar eclipse of 2026 will occur on Tuesday, February 17.
- It is an annular solar eclipse, popularly called the Ring of Fire eclipse.
- The Moon will cover up to 96 percent of the Sun’s central disk.
- The annular phase may last up to 2 minutes and 20 seconds.
- The eclipse will be fully visible mainly in Antarctica.
- Partial visibility will occur in southern Africa, southern South America, Madagascar and Mauritius.
- The eclipse will not be visible anywhere in India or most parts of Asia.
- Sutak Kaal rules do not apply in India as the eclipse will not be visible.
- A total lunar eclipse will follow on March 3–4, 2026.
- Future annular eclipses are scheduled for 2027, 2028 and 2030.
What Is an Annular Solar Eclipse and Why Is It Called the Ring of Fire?
A solar eclipse occurs when the Sun, Moon and Earth align in a straight line, a configuration known as syzygy. During an annular solar eclipse, the Moon is near its apogee, the farthest point from Earth in its orbit. Because the Moon appears slightly smaller than the Sun, it cannot block sunlight completely.
Also Read: ISRO Warns of Radio Blackouts as Powerful X8.3 Solar Flare Hits Earth, Satellites on High Alert
This leaves a thin, bright ring of sunlight visible around the Moon’s dark disk, creating the dramatic “Ring of Fire.” Daylight dims to a twilight-like brightness but does not turn completely dark because sunlight remains visible around the edges. Unlike total solar eclipses, the Sun’s corona is not visible during annularity, although brief effects such as Baily’s beads may appear at the beginning and end of the ring phase.
Date and Timings of the First Solar Eclipse of 2026
Astronomical sources provide slightly different phase timings depending on calculation models and observation locations. The eclipse will unfold over several hours globally on February 17, 2026.
| Eclipse Phase | Approximate Timing (UTC) |
| Partial Begins | Around 04:51 – 07:01 UTC (varies by source) |
| Annularity Starts | Around 06:05 UTC |
| Maximum Eclipse | Around 07:13 – 12:12 UTC (location dependent) |
| Annularity Ends | Around 08:21 UTC |
| Partial Ends | Around 09:35 UTC |
The annular phase itself will last up to about 2 minutes and 20 seconds, with approximately 96 percent of the Sun’s center covered by the Moon.
Will the February 17 Solar Eclipse Be Visible in India?
The annular solar eclipse will not be visible in India. The eclipse path lies far south of the equator, and during the event the Sun will be below the horizon across the Indian subcontinent. As a result, no partial or annular phase will be visible anywhere in India or most of Asia.
Since the eclipse is not visible in India, traditional religious observances related to eclipses, including Sutak Kaal, are not considered applicable. Temples will remain open, daily rituals and pujas can continue normally, and no fasting is required specifically for this eclipse.
Where Will the Ring of Fire Eclipse Be Visible?
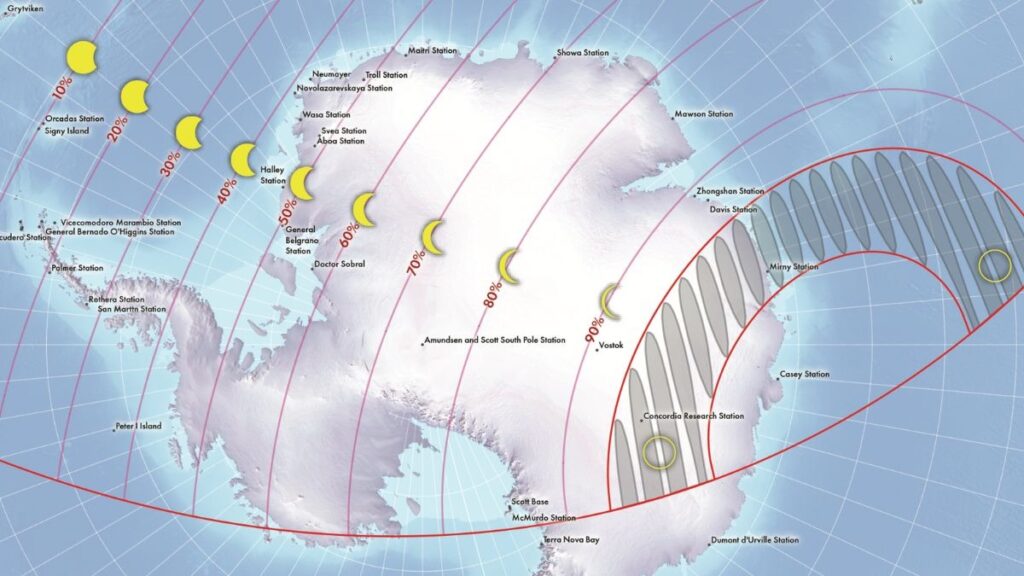
The path of annularity stretches approximately 4,282 kilometers in length and about 616 kilometers in width, crossing western Antarctica and skimming the Davis Sea coast of the Southern Ocean. The Moon’s antumbral shadow will cross Earth in about 59 minutes.
Full Annular Visibility
- Antarctica, especially inland regions
- Concordia Research Station (French–Italian facility)
- Mirny Station on the Davis Sea coast
Only a very small number of people, mainly scientists stationed in Antarctica, are expected to witness the full Ring of Fire. Experts noted that only two inhabited locations fall within the annular path, and neither is set up for tourism.
Cloud cover may also affect visibility. Around 65 percent cloud cover is expected near Mirny Station, compared with roughly 35 percent over mainland Antarctica, giving Concordia a better chance of clear observation. Temperatures at Concordia can drop to minus 80 degrees Celsius, making observation conditions extremely challenging.
Partial Visibility Regions
- Southern Africa including South Africa, Mozambique, Zimbabwe and Tanzania
- Southern parts of Argentina and Chile
- Madagascar and Mauritius
- Parts of the Pacific, Indian, Atlantic and Southern Oceans
Some locations will see only a small portion of the Sun covered, appearing as if a bite has been taken out of it.
Visibility Percentage in Selected Locations
| Location | Sun Covered |
| Heard & McDonald Islands | 88% |
| French Southern & Antarctic Lands | 88% |
| Port Louis, Mauritius | 32% |
| Saint-Denis, Reunion | 31% |
| Antananarivo, Madagascar | 20% |
| Durban, South Africa | 16% |
| Maputo, Mozambique | 13% |
| Maseru, Lesotho | 11% |
| Gaborone, Botswana | 4% |
| Harare, Zimbabwe | 3% |
| Ushuaia, Argentina | 3% |
Safety Guidelines for Observing the Solar Eclipse
Astronomers emphasize that it is unsafe to look directly at the Sun during any phase of a solar eclipse without proper eye protection. Observers must use ISO 12312-2 certified eclipse glasses or approved solar filters for telescopes and cameras. Sunglasses or regular glasses are not safe and may cause permanent eye damage.
The Cosmic Sequence Continues: Lunar Eclipse and Future Events
About two weeks after the annular solar eclipse, a total lunar eclipse on March 3–4, 2026 will turn the Moon red for approximately 58 minutes. Nearly 31 percent of the world’s population, around 2.5 billion people, will be able to see this event.
The next annular solar eclipse will occur on February 6, 2027, visible from Chile, Argentina, Uruguay, Brazil and parts of West Africa. Additional annular eclipses are scheduled for 2028 and 2030 across parts of South America, Europe, North Africa and Asia.
Understanding Cosmic Events Through True Spiritual Knowledge
Astronomical events like solar eclipses reflect the precise order and discipline governing the universe. According to the unique spiritual knowledge explained by Saint Rampal Ji Maharaj, natural phenomena occur under fixed divine laws created by the Supreme Power. Such understanding helps remove fear, myths, and superstition often associated with eclipses, encouraging people to view these events with awareness and rational understanding.
This perspective connects scientific observation with spiritual wisdom, guiding individuals toward truth, inner clarity, and a balanced life rooted in knowledge rather than belief or fear.
A Rare Astronomical Event That Highlights the Precision of Celestial Motion
The annular solar eclipse of February 17, 2026 demonstrates the remarkable precision of celestial mechanics as the Sun, Moon and Earth align to create a rare visual phenomenon. Although India will not witness the Ring of Fire directly, the event remains significant for scientific observation and global skywatching communities.
With most of the annular path passing over remote Antarctic regions, only a small number of observers will experience the eclipse in person. For others, live scientific coverage and global broadcasts will provide an opportunity to witness one of nature’s most fascinating astronomical displays.
FAQs on Annular Solar Eclipse February 17, 2026
1. Will the Annular Solar Eclipse on February 17, 2026 be visible in India?
No, the Annular Solar Eclipse on February 17, 2026 will not be visible in India because the eclipse path lies in the Southern Hemisphere.
2. Why is the February 17, 2026 solar eclipse called the Ring of Fire?
It is called the Ring of Fire because the Moon appears smaller than the Sun, leaving a bright ring of sunlight visible around the Moon.
3. Where will the Ring of Fire solar eclipse be visible in 2026?
The annular phase will be visible mainly in Antarctica, while partial eclipse visibility will occur in southern Africa, southern South America, Madagascar and nearby regions.
4. What time will the Annular Solar Eclipse February 17, 2026 occur?
The eclipse will occur on February 17, 2026, with different phases beginning around early morning UTC and varying depending on geographic location.
5. Is it safe to watch an annular solar eclipse with naked eyes?
No, viewing an annular solar eclipse without certified eclipse glasses or solar filters is unsafe and can cause permanent eye damage.
















